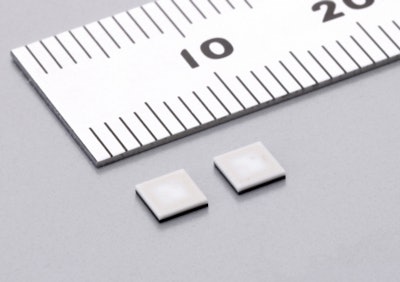
Murata Launches World's Smallest HF-Band RFID Tag for Faster Reading of More Data
KYOTO, Japan - Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd. is going to launch mass production of the world's smallest HF-band RFID *1 tag (3.2x3.2x0.7mm). Murata has applied its proprietary multi-layer circuit board technology and high-frequency module technology, with which the successful miniaturization of an RFID tag to one-tenth the size of an RFID tag composed of plane surface, was achieved.
The company will exhibit this product at "CEATEC JAPAN 2012", which will be held at Makuhari Messe in Chiba Prefecture from October 2 nd to 6 th, 2012.
"This innovative RFID tag is an ultra-small component that has been developed by integrating multi-layer circuit board and high-frequency module technologies, Murata core competencies." says Mr. Hideharu Ieki, Executive Vice President Technology & Business Development Unit Member of the Board of Directors. "In addition to contactless IC cards, which are rapidly becoming widespread, this RFID tag can be attached to various objects to provide, for example, connections with a smartphone. Murata intends to respond flexibly to various potential customer needs and new application use cases in various fields."
RFID *2 indicates technologies in general that exchange information using near-field wireless communications from an IC tag embedded with ID data. Recently, RFID is being used for contactless IC cards such as prepaid fare cards on train lines and e-money, significantly increasing the convenience of our lifestyles. Murata introduced the RFID device "MAGICSTRAP ®" to the market in 2008. Until now, "MAGICSTRAP ®" has been used for manufacturing process management and other applications.
Normally, an RFID device consists of an IC tag and antenna. Because the HF-band RFID tag uses low frequencies, the size of the RFID antenna tends to become extremely large. Therefore, it is believed that there is a limit to miniaturization of RFID devices. In an effort to resolve this issue, Murata applied multi-layer circuit board and high-frequency module technologies that the company has developed over the years to configure the antenna inside the ceramic substrate. As a result, it has successfully miniaturized an RFID tag to one-tenth the size of the RFID tag composed of plane surface. Furthermore, the new RFID product uses a ceramic module structure that makes it highly resistant to the environment and enables it to achieve stable operation under various environmental conditions.
Features
-- World's smallest RFID tag operating in the HF band
-- Can be attached to various objects
-- Easy to apply since no antenna design is required
-- Extremely high resistance to environmental conditions (high temperature, high humidity)
-- Compliant with ISO 15963 standard *3. Can use an ISO 15963 standard-compliant reader/writer *4 to read and write data from internal memory.
-- Use of ICODE SLIX IC manufactured by NXP Semiconductors
Applications
Small appliance/object tracking, management, certification, authentication, etc.
Electric characteristics
Read range: 15mm (Reader/writer output: 200mW, antenna size: 35x54mm)
External Size
3.2×3.2×0.7mm
Production
Mass production starts at Fukui Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd. from October (1,000,000 units per month).
Sample price
100 yen/unit
Terminology
*1 HF-band RFID: A HF-band RFID tag operates at 13.56MHz, which is the frequency band used by general contactless IC cards. This HF-band IC tag is widely used at present.
*2 RFID: Acronym of Radio Frequency Identification. RFID devices are used for exchanging information via near-field wireless communications that utilize electromagnetic fields or electric waves to transfer data from an IC tag embedded with ID data. Using this technology, information can be stored in a small component and read from a distant location. Compared with barcodes, RFID has the advantages of a much larger read-range, multiple tags can be read simultaneously, and information can be rewritten. RFID tags are already being used for inventory management in the distribution industry and management of work in process in the plant.
*3 ISO 15963 standard: International standard that defines the ID specifications of wireless IC tags.
*4 Reader/writer: A device that reads and writes data by communicating with a wireless IC tag via an antenna.
Murata in Brief
Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd. is a worldwide leader in the design, manufacture and sale of ceramic-based passive electronic components & solutions, communication modules and power supply modules. With annual revenues of ¥585 billion (~$7.1B USD), Murata is committed to the development of advanced electronic materials and leading edge, multi-functional, high-density modules. The company has employees and manufacturing facilities throughout the world. For more information, visit Murata's website at http://www.murata.com/






















